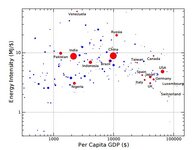
An
electric arc furnace (
EAF) is a
furnace that heats material by means of an
electric arc.
Industrial arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one-tonne capacity (used in
foundries for producing
cast iron products) up to about 400-tonne units used for secondary
steelmaking. Arc furnaces used in research laboratories and by
dentists may have a capacity of only a few dozen grams. Industrial electric arc furnace temperatures can reach 1,800 °C (3,300 °F), while laboratory units can exceed 3,000 °C (5,400 °F).
In electric arc furnaces, the charged material (the material entered into the furnace for heating, not to be confused with
electric charge) is directly exposed to an electric arc, and the current from the electrode terminals passes through the charged material.Arc furnaces differ from
induction furnaces, in which the charge is heated instead by
eddy currents.